The somatic cells of the human body are capable of a large number of mitotic divisions.It is thanks to this feature of our body that it can exist independently for a long time in the external environment, restore damaged tissues or dead cells.
Unfortunately, the number of these divisions is strictly limited and individual for each person.In this sense, upon reaching old age, several diseases begin to appear.Arthrosis is considered one of the most common, as it is the painful syndrome that accompanies this pathology that significantly reduces the patient's quality of life.
Omarthrosis, or osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint, becomes a serious problem that interferes with normal work performance and daily tasks.It is this disease that will be discussed below;we will analyze the causes of arthrosis of the shoulder joint, the symptoms and treatment of this unpleasant pathology.
What is it?
Shoulder arthrosis is accompanied by a disruption of the normal blood supply to this important bone joint, as a result of which the cartilage tissue decreases in thickness and the head of the bone is exposed.Due to the increase in friction, the person notices the appearance of pain which, depending on the degree, may only appear during physical activity or even at rest.
Due to the damage to neighboring anatomical structures, an inflammatory process is observed, worsening the decrease in the range of active and passive movements of the upper limb.Lack of adequate treatment often leads to a complication of the process due to joint deformation, which is called deforming osteoarthritis.
Anatomy of the shoulder joint
The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint;It is this structure that allows the person to perform different movements with the upper limb.Three large bones converge in this anatomical region, including the scapula, the clavicle and the humerus itself.The joint capsule is quite deep and reinforced by a whole complex of ligaments.
Due to some anatomical features of the structure of the shoulder joint, cases of spontaneous dislocations and subluxations of this area during daily work at home are common.The ease and variety of movements are due not only to the spherical shape of the articular surfaces, but also to the presence of a large amount of special synovial fluid, which reduces friction between the surfaces.
Causes of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint
The disease presented in the article develops as a result of the influence of a whole complex of provoking factors.Clinical studies carried out in several leading research institutes made it possible to reliably establish the pathophysiological mechanism of the appearance of changes in bone and cartilage tissue during arthrosis.However, reliable “triggers” have never been identified.
In most cases, this degenerative disease develops secondarily, that is, after some pathogenic effect on the shoulder joint.
A retrospective analysis of the medical histories of patients with this pathology in the shoulder joint region made it possible to identify influences that could significantly increase the probability of the disease occurring.
These include:
- excessive physical activity leading to physical thinning of the articular surfaces;
- frequent falls on the arm and other injuries to the waist of the upper limbs;
- occupational risks;
- congenital connective tissue pathologies;
- impaired mineral metabolism, accompanied by the appearance of crystalloid deposits on the head of the humerus;
- decreased production of synovial fluid;
- age-related changes in the structure of the vascular wall, causing dystrophic changes in the bone;
- lack of adequate drug therapy in the presence of an acute or chronic inflammatory process in the joint space;
- pathologies of the nervous system that induce insufficient trophism of the musculoskeletal system;
- presence of excess weight, constant swelling of the upper extremities;
- diseases of the endocrine system.
Primary osteoarthritis of the shoulder
The modern medical classification of arthrosis of the shoulder joint, depending on the causes of development, distinguishes two forms - primary and secondary.In the case of primary, the diagnosis is established only after carrying out a full range of diagnostic measures to completely exclude the presence of the above-described causes of the onset of the disease.The starting point in pathogenesis is believed to be the deterioration of blood flow throughout the system against the background of a decrease in myocardial contractility or the permeability of the vascular wall.
Over time, a person begins to notice the appearance of unpleasant sensations during shoulder movements.At first, the discomfort is present during exercise and then stops disappearing even during rest.Another reason that contributes to the rapid progression of the disease is the appearance of so-called osteophytes.These bone spurs are formed as a result of a compensatory increase in chondroclast activity that attempts to replace the loss of mature cartilaginous cells.They have the appearance of a tip that, when moving, contributes to damage to the capsule and the occurrence of an aseptic inflammatory process.
Against the background of the described changes, fibrin threads appear in the synovial fluid, permeating the ligamentous apparatus during prolonged rest.Due to a decrease in the elasticity of white muscle fibers, a characteristic feeling of “stiffness” appears, which usually disappears after 20-30 minutes of limb development.Shoulder arthrosis presents pronounced symptoms, its intensity and treatment are directly proportional to the degree of the development process.
Secondary arthrosis of the shoulder joint
The secondary form of this disease is a consequence of the presence of an underlying pathology, complicated by disturbances in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system.Among the causes, traumatic injuries of an acute or chronic nature come first in frequency.This problem is especially relevant in the cold season, when a person often falls, reaching out to break the fall.
Enzymopathies are congenital diseases accompanied by a decrease in the production of specific enzymes that make up the ligamentous apparatus and can also cause the development of secondary osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint.It is these patients who often experience dislocations and subluxations when carrying out everyday activities.Laxity in this bone joint contributes to increased trauma to the contact surfaces, against which the disease arises.
Symptoms and signs
Shoulder osteoarthritis presents complex symptoms and treatment;Due to some features of the characteristic signs, their detection often occurs in the later stages of the development of the pathological process.Experts distinguish three degrees of destruction of the cartilaginous tissue of the girdle of the upper limbs.According to them, the symptom complex found in the patient will also be different.
In stage 1 of the disease, the person rarely feels pain in the shoulder;Most of the time there is discomfort in the limb during heavy physical exercise or immediately after.In these situations, the patient needs several days to recover and completely get rid of the discomfort in the joint.It is precisely for this reason that a person tends to attribute pain to the manifestation of a simple, as it seems to him, sprain of the ligamentous apparatus, which the disease continues its development, remembering more and more often.
Arthrosis of the shoulder joint of the 2nd degree is accompanied by a more vivid clinical picture.This is due to the fact that, in addition to erosion and disruption of the normal nutrition of the articular surfaces, secondary inflammation occurs, spreading to the surrounding ligaments and muscle fibers.The disease leads to the fact that pain is present even with small physical exertion.Due to severe pain, the patient becomes unable to perform circular movements, which indicates that the osteoarthritis deformation process has already begun and the range of active movements of the hand in space is limited.
The development of grade 3 leads to an almost complete loss of mobility in the shoulder joint.The patient notes significant muscle atrophy and loss of the ability to care for himself.Another characteristic symptom is the appearance of bony protrusions above the surface of the skin.The likelihood of the disease going this far exists mainly in people who do not have the opportunity to minimize the load on their upper limbs due to professional activity or during professional sports.
Diagnosis of arthrosis of the shoulder joint
Establishing the diagnosis of arthrosis of the shoulder joint is a procedure that requires certain skills from the specialist.After the appearance of pain in the upper limb, it is advisable to consult an orthopedic traumatologist.It is the doctors of this profile who have all the necessary knowledge.
During the examination, the first thing you should pay attention to is the patient's complaints and medical history.The doctor finds out why the pain appeared, what its nature is, and also after what it disappears.Next, it is necessary to identify occupational risks and the presence of risk factors.
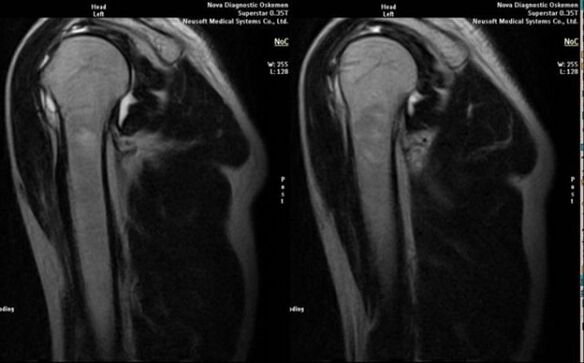
The main diagnostic method for detecting deforming osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint is plain radiography.
The next step is the physical examination, when the specialist uses palpation to identify painful areas and determine the full range of active and passive movements of the limb.In addition, the presence of local edema and increased skin temperature in the area of the bone joint projection are assessed.Based on the data obtained, the doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis, but a differential diagnosis is necessary to prescribe the most appropriate therapy.
To establish the most correct diagnosis, the extent of the process and the possible identification of the cause, a number of additional laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are performed on the patient.
The most informative include:
- clinical blood test;
- determination of biochemical parameters of blood serum;
- clinical urine analysis;
- X-ray of the affected joint;
- ultrasound diagnosis;
- arthroscopic examination;
- magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography;
- scintigraphy;
- joint puncture followed by biochemical analysis of synovial fluid.
Signs that directly indicate the development of arthrosis include the appearance of significant narrowing of the joint space, sclerosis of subcartilaginous structures, thinning of the chondrocyte layer itself, appearance of osteophytes and deposition of salt crystals in the intra-articular fluid.
How to treat osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint
After establishing this diagnosis, the doctor is faced with a serious doubt about choosing the most appropriate therapeutic tactic.Modern medicine has reached a level where it is able to help patients with diseases of the musculoskeletal system to completely return to normal life.
Treatment of arthrosis of the shoulder joint is long-term and therefore often leads to the development of complications.
The method chosen to correct arthrosis of the shoulder joint directly depends on the following factors:
- degree of process;
- general condition of the patient;
- age;
- physiological characteristics.
As a rule, in the initial stages, it is enough to prescribe medications of general and local action.
In the presence of second-degree arthrosis of the shoulder joint, the symptoms accompanying the disease are almost impossible to completely stop.A person shows a significant reduction in physical activity in order to prevent the development of the pathological process;in parallel, a whole range of medications is prescribed.
The third degree practically does not lend itself to conservative influence;In the presence of such an advanced disease, surgical treatment is indicated, the volume of which depends on many factors and is chosen directly by the attending physician.Next, we will talk in more detail about each of the existing methods for getting rid of osteoarthritis.
Medicines
The following groups of drugs are used as conservative therapy in the presence of this disease:
- glucocorticoids;
- non-steroidal medicines with anti-inflammatory effects;
- analgesics;
- medicines with chondroprotective effects.
Medicinal substances belonging to this group have a significantly more pronounced anti-inflammatory effect than non-steroidal medicines.
Glucocorticoids are recognized as the most effective agents against inflammatory phenomena.These natural and synthetic analogues of adrenal hormones can significantly influence the production of inflammatory neurotransmitters.This reduces local swelling, pain and temperature in the affected area of the musculoskeletal system.
The disadvantages of this treatment include a large number of side effects of glucocorticoids.The presented drugs can cause Cushing's syndrome, lead to disruption of general metabolism and water retention in the intercellular space.In this sense, it is recommended to start treatment with prescription NSAIDs.
Nonsteroidal medications with anti-inflammatory effects have a direct effect on cyclooxygenase molecules, which induce inflammation in injured tissues.
Preference is given to selective drugs that do not have a harmful effect on the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.
Depending on the severity of the patient's condition and the severity of the pain syndrome, narcotic and non-narcotic analgesics are used.
The first group is considered more effective, but the side effect of drug addiction leads to the need to strictly limit its use.
Non-opioid medications have a less pronounced analgesic effect, but are not addictive and can be prescribed more widely.
It is extremely important not to use chondroprotective agents during the acute period of the disease, as this can lead to an increase in inflammatory processes.It is necessary to stop the attack, and then prescribe a long course of medications that restore the structure of the joint.
Surgical treatment
In some cases, surgical correction of a patient with shoulder osteoarthritis is indicated.This invasive method is used in the presence of a serious destructive process directly in the joint.Most of the time, patients undergoing surgical treatment are unable to perform daily tasks due to severe limitation of active and passive shoulder movements.
After the final diagnosis has been established, a whole series of measurements are taken, during which the ideal parameters for the future prosthesis are selected.Then, a transplant made of high-strength polymers or titanium is made to order.

Surgery for arthrosis of the shoulder joint is performed in the terminal (last) stages of the disease.
The surgical intervention is quite extensive, so the patient goes through a long period of preparation.A complete replacement of the affected bone joint is performed, followed by a period of physiotherapy, which allows full functionality of the girdle of the upper limb to be restored.
Therapeutic exercise
It is physical exercises that allow you to restore shoulder mobility in the shortest possible time, not only after surgical treatment, but also during the course of medicinal influence on the disease.Specially developed complexes relieve morning stiffness, stimulate the normalization of blood supply, lymphatic drainage and restore the normal composition of synovial fluid.
It is extremely important that rotation and adduction movements of the upper limb are performed without additional loads, otherwise there is a high probability of additional trauma and cartilage destruction.Rehabilitation specialists are engaged in the development of special physiotherapy complexes.
Each clinical case requires an individual approach, so if you have a disease or want to prevent its development, seek help from this doctor.
Recommendations for home treatment
Any illness must be treated in a hospital environment, under the supervision of highly qualified medical professionals.However, in some cases, the patient does not have the opportunity to stay at the clinic for a long time.In such situations, you need to independently monitor your recovery process.

Physical exercises for deforming osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint are extremely important because they slow the progression of the disease.
The following recommendations must be followed:
- strictly follow the instructions and prescriptions of the attending physician;
- limit physical activity of the affected arm as much as possible;
- get rid of excess body weight by creating a slight calorie deficit and walking in the fresh air;
- divide the daily amount of food into 5 to 6 meals;
- drink at least 2 liters of water daily;
- change the type of work activity to one that requires minimal load on the upper limbs.
Folk remedies
Many elderly people know from experience what osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint is and how to treat it at home.In addition to the recommendations described above regarding changing the type of work activity and eliminating excess body weight, traditional medicine has a whole range of healing agents that help reduce pain and swelling in the affected limb.For this purpose, various ointments, decoctions, compresses and baths are used.It is these treatment methods that we will cover in more detail.
Ointments
Alternative medicine has a large number of original and effective recipes for preparing anti-inflammatory ointments.The simplest method involves mixing one egg yolk with a teaspoon of turpentine and the same amount of apple cider vinegar.Applying the ointment to the affected joint at night will significantly reduce pain and inflammation.

Another good remedy for treating osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint is a mixture of fifty grams of elecampane and one hundred milliliters of vodka.After mixing the components and letting them brew for 12 days, you should rub the resulting ointment into the projection area of the inflamed bone joint every day.
Decoctions and tinctures
Decoctions and tinctures play a fundamental role in folk medicine.One of the easiest to prepare and at the same time most effective infusions for arthrosis is considered to be a mixture of a tablespoon of ground agave leaves with 150 milliliters of 70% ethyl alcohol.After infusing the medicine for two weeks, the liquid must be consumed orally, twenty drops with water, for thirty days.
For fans of decoctions there is a good remedy.To prepare it you will need two tablespoons of blueberry leaves and half a liter of boiling water.After mixing the ingredients, let them ferment in a thermos overnight.Then, take 150 ml of the product three times a day, immediately before meals.The course of treatment is 30 days.
Compresses and friction
To reduce pain and inflammation in the area of the shoulder joint affected by osteoarthritis, various compresses are used.One of the most effective is considered to be a mixture of one liter of vodka and one hundred grams of cinquefoil.The medicine must be infused for two weeks, after which it must be used every night before bed.
Another simple and effective remedy is a compress made up of finely grated horseradish, mixed with a little water until it forms a puree.Place a handful of medicine in gauze and apply it to the inflamed joint for 20 to 30 minutes.

Baths
Baths are widely used in the treatment of various diseases of the musculoskeletal system.Thanks to the complex effect, a good anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effect is achieved.
Preparing the bath is quite simple;To do this, follow these recommendations:
- fill the bathtub with hot water;
- add about a kilogram of sea or common kitchen salt;
- throw some pine branches;
- add a few teaspoons of crystallized honey;
- at the end, add a teaspoon of turpentine oil.
The course of treatment consists of twelve baths.The duration of one procedure should be approximately twenty minutes.From the first use of the therapeutic bath, the patient notices a significant improvement in their general condition and a reduction in joint discomfort.
Prevention
Modern medicine does not yet have specific measures to prevent osteoarthritis.This is due to the polyetiological nature of the pathology.However, there are non-specific measures that can significantly reduce the risk of developing the disease.There are primary and secondary prevention.
The first includes:
- daily walks in the fresh air;
- the use of a contrast shower, which allows you to increase vascular tone;
- gentle joint treatment, avoiding excessive physical activity;
- moderate exercise 2-3 times a week.
The second group includes the following:
- complete and comprehensive treatment of arthritic processes;
- regular intake of calcium supplements;
- prescription of chondroprotective medications;
- physiotherapy.


















